Cost To Put Solar On House

The cost of putting solar on a house is a question on many homeowners’ minds. The transition to solar energy offers significant long-term savings and environmental benefits, but understanding the initial investment is crucial. This guide delves into the multifaceted aspects of solar panel installation costs, exploring everything from the price of individual components to available incentives and financing options. We’ll examine various factors influencing the total cost, including system size, panel type, geographical location, and the installation process itself. By the end, you’ll have a clearer picture of what to expect and how to make informed decisions about embracing solar power for your home.
We will dissect the various cost components, including panels, inverters, racking, wiring, permits, and labor, comparing different panel types and system sizes. Furthermore, we’ll explore the landscape of financial incentives—federal, state, and local—and analyze different financing methods such as loans, leases, and Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs). A realistic timeline for installation will be provided, along with an overview of maintenance and long-term costs. Finally, we will compare the overall cost-effectiveness of solar energy against traditional energy sources, highlighting the long-term financial and environmental advantages.
Factors Influencing Solar Panel Installation Costs
The cost of installing solar panels on your house is influenced by a variety of factors. Understanding these factors will help you make informed decisions and budget effectively. This section provides a detailed breakdown of the key cost components, including materials, labor, and permitting.
Cost Breakdown of Solar Panel Installation, Cost to put solar on house

Source: scopenew.com
Several components contribute to the overall cost of a solar panel installation. These include the solar panels themselves, the inverter, racking system, wiring, permits, and labor costs. Let’s examine each one in detail.
- Solar Panels: This is typically the largest expense, varying depending on panel type, efficiency, and wattage. Monocrystalline panels are generally the most expensive, followed by polycrystalline, and then thin-film.
- Inverter: The inverter converts the DC electricity generated by the panels into AC electricity usable in your home. The cost depends on the system’s size and efficiency.
- Racking System: This system mounts the panels to your roof, and the cost varies based on roof type and complexity.
- Wiring and Conduits: These connect the panels, inverter, and your home’s electrical system. Costs depend on the distance and complexity of the wiring runs.
- Permits: Necessary permits and inspections add to the overall cost and vary by location.
- Labor: Installation labor accounts for a significant portion of the total cost. The complexity of the installation (roof access, roof type, etc.) influences labor costs.
Cost Variations Between Solar Panel Types
Different types of solar panels offer varying levels of efficiency and cost. Monocrystalline panels are the most efficient but also the most expensive. Polycrystalline panels offer a balance between efficiency and cost, while thin-film panels are the least expensive but also the least efficient.
- Monocrystalline: Highest efficiency, longest lifespan, highest cost.
- Polycrystalline: Moderate efficiency, good lifespan, moderate cost.
- Thin-film: Lowest efficiency, shorter lifespan, lowest cost.
Impact of System Size (kW) on Installation Price

Source: homesteadingalliance.com
The size of your solar panel system, measured in kilowatts (kW), directly impacts the installation cost. Larger systems generate more electricity but also cost more upfront. The following table provides estimated costs, energy production, and payback periods for different system sizes. These are estimates and will vary based on location, incentives, and other factors.
| System Size (kW) | Estimated Cost (USD) | Annual Energy Production (kWh) | Estimated Payback Period (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 kW | $15,000 – $25,000 | 6,000 – 8,000 | 7-12 |
| 7 kW | $21,000 – $35,000 | 8,400 – 11,200 | 6-10 |
| 10 kW | $30,000 – $50,000 | 12,000 – 16,000 | 5-8 |
| 15 kW | $45,000 – $75,000 | 18,000 – 24,000 | 4-7 |
Geographical Location’s Influence on Costs
Geographical location significantly affects both material and labor costs. Areas with high demand for solar installations may have higher labor costs due to increased competition and higher material costs due to transportation and import fees. Areas with abundant sunshine might offset some of these costs with higher energy production.
Incentives and Financing Options

Source: currenthome.com
Reducing the upfront cost of solar panel installation is achievable through various incentives and financing options. This section explores the available financial assistance and financing methods to help you make an informed decision.
Available Incentives
Several federal, state, and local incentives can significantly reduce the initial investment in solar energy. These incentives often include tax credits, rebates, and other financial programs. It is crucial to research the specific incentives available in your area, as they vary considerably.
- Federal Tax Credit: The federal government offers a significant tax credit for residential solar installations. The exact percentage may change, so it’s essential to check the current IRS guidelines.
- State and Local Incentives: Many states and local governments offer additional rebates, tax credits, or other financial incentives to promote solar energy adoption.
Financing Methods
Several financing options are available for solar panel installations, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these options is crucial for choosing the best financial strategy for your needs.
- Loans: Similar to other home improvement loans, solar loans allow you to finance the installation and repay the loan over a set period with interest.
- Leases: With a lease, you don’t own the solar panels, but you pay a monthly fee to use the electricity they generate. At the end of the lease term, you may have the option to purchase the system.
- Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs): Under a PPA, a third party owns and maintains the solar panels, and you purchase the electricity they generate at a predetermined rate.
Comparison of Financing Options
Each financing method has its pros and cons concerning long-term financial implications. Loans provide ownership but require upfront payments and interest. Leases and PPAs have lower upfront costs but might result in higher long-term expenses.
- Loans: Pros: Ownership, potential tax benefits; Cons: Higher upfront costs, interest payments.
- Leases: Pros: Low upfront cost; Cons: No ownership, potentially higher long-term costs.
- PPAs: Pros: No upfront cost, minimal maintenance responsibility; Cons: No ownership, limited control over energy production.
Realistic Payback Periods
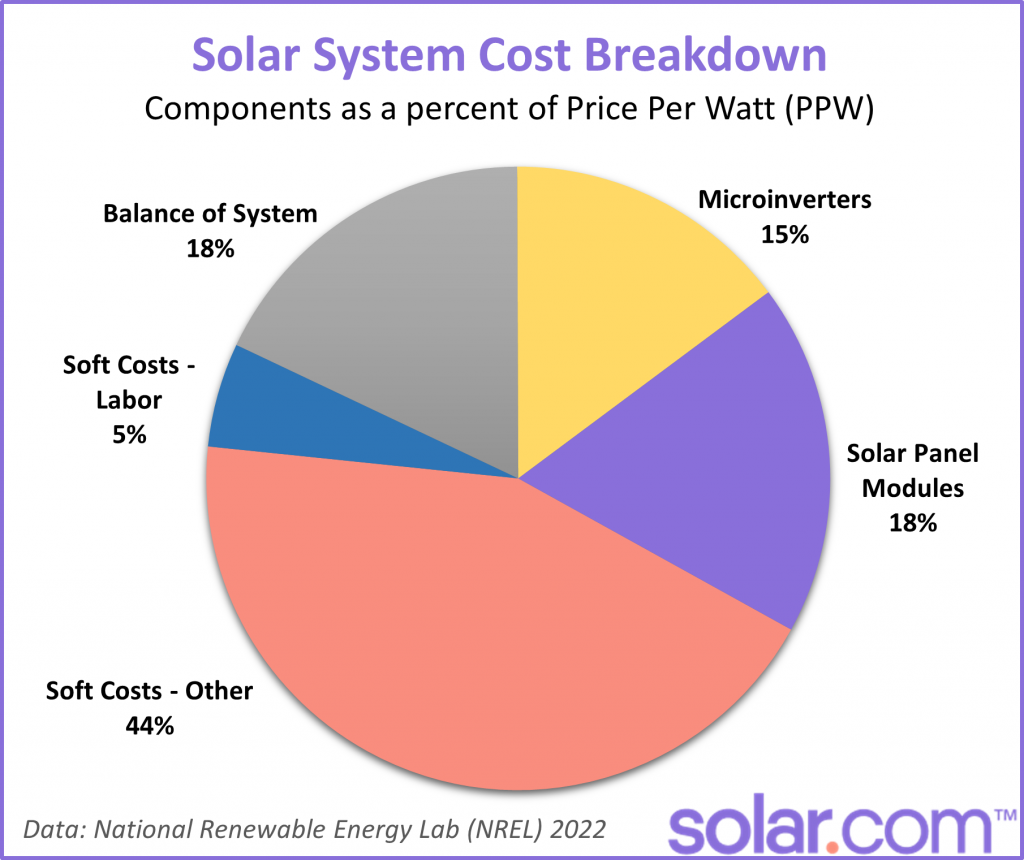
Source: solar.com
Payback periods vary significantly depending on factors such as system size, incentives, electricity rates, and financing options. For example, a 5kW system with a high level of incentives and low electricity rates might have a payback period of 5 years, while a larger system with fewer incentives and high electricity rates might take 10 years or more.
Installation Process and Timeline
The solar panel installation process involves several steps, from initial assessment to final connection. Understanding this process helps you manage expectations and anticipate potential challenges.
Steps Involved in Solar Panel Installation
A typical solar panel installation involves several key stages. Each stage has a specific timeline and potential challenges that could affect the overall project.
- Initial Assessment and Design: A solar installer will assess your energy needs, roof suitability, and shade conditions to design a customized system.
- Permitting and Approvals: The installer will obtain the necessary permits from your local authorities.
- Equipment Procurement: The installer will order and receive the solar panels, inverter, and other necessary equipment.
- Installation: The installation crew will mount the panels, install the inverter, and connect the system to your home’s electrical panel.
- Inspection and Connection: Once the installation is complete, an inspection will be conducted, and the system will be connected to the grid.
Realistic Timeline
The total timeline for a solar panel installation typically ranges from several weeks to a few months, depending on the system size, permitting processes, and weather conditions. Delays can occur due to permitting issues, equipment availability, or unforeseen circumstances.
Potential Challenges and Delays
Several factors can cause delays or increase costs. These include complex roof designs, permitting issues, equipment shortages, or unfavorable weather conditions. Open communication with your installer is crucial to address any potential challenges promptly.
Flowchart Illustrating the Installation Process
A flowchart visually represents the installation process, highlighting key decision points and sequential steps. This ensures a clear understanding of the project’s progression.
[Imagine a flowchart here showing the steps Artikeld above, with decision points like “Roof suitable?” or “Permits approved?” branching to different paths.]
Maintenance and Long-Term Costs: Cost To Put Solar On House
While solar panels are durable and require minimal maintenance, understanding the potential long-term costs is essential for responsible budgeting. This section Identifies typical maintenance requirements and associated expenses.
Typical Maintenance Requirements
Solar panels and inverters generally require minimal maintenance. Regular inspections and occasional cleaning are typically sufficient to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Potential Repair or Replacement Costs
Over the system’s lifespan (typically 25-30 years), you might encounter repair or replacement costs. These could include replacing damaged panels, repairing faulty inverters, or addressing wiring issues. The costs will vary depending on the extent of the damage and the age of the components.
Realistic Estimates of Long-Term Maintenance Expenses
Annual maintenance costs are typically low, ranging from a few hundred dollars for cleaning and inspections. However, unexpected repairs can significantly increase these costs.
Expected Maintenance Tasks, Frequency, and Costs
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Estimated Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Panel Cleaning | 1-2 times per year | $50 – $200 |
| Inverter Inspection | Annually | $100 – $200 |
| System Inspection | Annually | $150 – $300 |
| Panel Replacement (per panel) | As needed | $300 – $800 |
| Inverter Replacement | As needed | $1,000 – $3,000 |
Comparing Solar to Other Energy Sources
Comparing the cost of solar energy to traditional energy sources helps determine its long-term cost-effectiveness and environmental impact. This section analyzes the cost and environmental implications of different energy sources.
Cost Comparison
The cost of solar energy varies depending on factors discussed earlier, but it generally becomes more cost-competitive with traditional electricity sources over time. The initial investment is higher, but the long-term savings on electricity bills can outweigh the upfront costs.
Long-Term Cost Savings

Source: blueandgreentomorrow.com
Solar energy significantly reduces or eliminates electricity bills, leading to substantial long-term savings. The extent of these savings depends on your energy consumption, electricity rates, and the size of your solar panel system.
Environmental Impact

Source: shopify.com
Solar energy is a cleaner and more sustainable energy source compared to traditional sources like grid electricity (often generated from fossil fuels) and natural gas. It significantly reduces carbon emissions and contributes to a healthier environment.
Cost-Effectiveness Scenarios
The cost-effectiveness of solar energy depends on several factors, including energy consumption, electricity rates, and the availability of incentives. A household with high energy consumption and high electricity rates will generally see a faster return on investment compared to a household with low energy consumption and low electricity rates.
For example, a household in California with high electricity rates might see a quicker payback period compared to a household in a state with lower electricity rates and fewer incentives. Detailed financial modeling for specific scenarios is recommended for precise cost comparisons.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the average lifespan of solar panels?
Solar panels typically last 25-30 years, although they may continue to produce power beyond that timeframe, albeit at reduced efficiency.
How much does it cost to replace a damaged solar panel?
The cost to replace a single damaged panel varies depending on the panel type and labor costs but generally ranges from a few hundred to over a thousand dollars.
Do I need to get permits for solar panel installation?
Yes, most jurisdictions require permits for solar panel installations. Check with your local authorities for specific requirements.
What is the impact of shading on solar panel performance?
Shading can significantly reduce the energy output of solar panels. Proper site assessment is crucial to minimize shading effects.
Can I sell excess solar energy back to the grid?
Many utility companies offer net metering programs that allow you to sell excess solar energy back to the grid, receiving credits on your electricity bill. Check with your local utility provider for details.
Comments are closed.